Explore web search results related to this domain and discover relevant information.

Note => REST is an architectural design style for APIs, while HTTP is the communication protocol used for data transfer over the web. REST APIs use HTTP methods to interact with resources, but they are not the same thing. REST defines how the APIs should behave, while HTTP defines the rules ...
Note => REST is an architectural design style for APIs, while HTTP is the communication protocol used for data transfer over the web. REST APIs use HTTP methods to interact with resources, but they are not the same thing. REST defines how the APIs should behave, while HTTP defines the rules for communication over the web.Your All-in-One Learning Portal: GeeksforGeeks is a comprehensive educational platform that empowers learners across domains-spanning computer science and programming, school education, upskilling, commerce, software tools, competitive exams, and more.In HTTP, there are five methods that are commonly used in a REST-based Architecture, i.e., POST, GET, PUT, PATCH, and DELETE. These correspond to create, read, update, and delete (or CRUD) operations, respectively.REST API stands for Representational State Transfer API. It is a type of API (Application Programming Interface) that allows communication between different systems over the internet.

REpresentational State Transfer (REST) is an architectural style. It is not a strict standard but provides certain guidelines and constraints. American computer scientist Roy Fielding originally…
REpresentational State Transfer (REST) is an architectural style. It is not a strict standard but provides certain guidelines and…This constraint tends to establish a technology coupling between the client and the web server. The client must be able to understand and execute the code it downloads on demand from the server. This is the only optional constraint for the REST architectural style.REST relies on stateless, cacheable, and client-server communication protocols like HTTP. By following the principles of REST and applying them to stateless protocols such as HTTP, developers can build API interfaces that can be used from any device or operating system.Statelessness is one of the key principles of a RESTful service. It dictates that a web server is not required to remember the state of the client application. All relevant contextual information should be sent by the client application in the request to the server for all its interactions.
A REST API is an application programming interface architecture style that conforms to specific architectural constraints, like stateless communication and cacheable data. It is not a protocol or standard.
REST APIs are one of the most common kinds of web interfaces available today. They allow various clients including browser apps to communicate with services via the REST API. Therefore, it's very important to design REST APIs properly so that we won't run into problems down the road.While REST APIs can be accessed through a number of communication protocols, most commonly, they are called over HTTPS, so the guidelines below apply to REST API endpoints that will be called over the internet.Even though some people think REST should only return hypertext (including Roy Fielding who created the term) REST APIs should accept JSON for request payload and also send responses to JSON. JSON is the standard for transferring data. Almost every networked technology can use it: JavaScript has built-in methods to encode and decode JSON either through the Fetch API or another HTTP client.To make sure that when our REST API app responds with JSON that clients interpret it as such, we should set Content-Type in the response header to application/json after the request is made. Many server-side app frameworks set the response header automatically.

REST (Representational State Transfer) is a software architectural style that was created to describe the design and guide the development of the architecture for the World Wide Web. REST defines a set of constraints for how the architecture of a distributed, Internet-scale hypermedia system, ...
REST (Representational State Transfer) is a software architectural style that was created to describe the design and guide the development of the architecture for the World Wide Web. REST defines a set of constraints for how the architecture of a distributed, Internet-scale hypermedia system, such as the Web, should behave.The REST architectural style emphasizes uniform interfaces, independent deployment of components, the scalability of interactions between them, and creating a layered architecture to promote caching to reduce user-perceived latency, enforce security, and encapsulate legacy systems.Roy Fielding was involved in the creation of these standards (specifically HTTP 1.0 and 1.1, and URI), and during the next six years he created the REST architectural style, testing its constraints on the Web's protocol standards and using it as a means to define architectural improvements — and to identify architectural mismatches.To create the REST architectural style, Fielding identified the requirements that apply when creating a world-wide network-based application, such as the need for a low entry barrier to enable global adoption.He also surveyed many existing architectural styles for network-based applications, identifying which features are shared with other styles, such as caching and client–server features, and those which are unique to REST, such as the concept of resources.
In REST architectural style, servers can temporarily extend or customize client functionality by transferring software programming code to the client. For example, when you fill a registration form on any website, your browser immediately highlights any mistakes you make, such as incorrect ...
In REST architectural style, servers can temporarily extend or customize client functionality by transferring software programming code to the client. For example, when you fill a registration form on any website, your browser immediately highlights any mistakes you make, such as incorrect phone numbers.The following are some of the principles of the REST architectural style:Find out what is RESTful API, how and why businesses use RESTful APIs, and how to use API Gateway with AWS.RESTful API is an interface that two computer systems use to exchange information securely over the internet. Most business applications have to communicate with other internal and third-party applications to perform various tasks.

REST, or Representational State Transfer, is an architectural style for building web services. It was first introduced by Roy Fielding in…
Understanding REST and RESTful APIs: Constraints, Methods, and Examples REST, or Representational State Transfer, is an architectural style for building web services. It was first introduced by Roy …In conclusion, REST is a popular architectural style for building web APIs. It is based on six constraints that ensure that REST APIs are scalable, fast, and reliable. REST APIs use HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE to perform operations on a resource.We have also shown code examples in Python, Node.js, Spring Boot, and C++ that demonstrate how to implement a simple REST API. By following the REST architectural style, you can build web APIs that are scalable, fast, and reliable, and that meet the needs of your clients.REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style for building web services.
This chapter introduces and elaborates the Representational State Transfer (REST) architectural style for distributed hypermedia systems, describing the software engineering principles guiding REST and the interaction constraints chosen to retain those principles, while contrasting them to ...
This chapter introduces and elaborates the Representational State Transfer (REST) architectural style for distributed hypermedia systems, describing the software engineering principles guiding REST and the interaction constraints chosen to retain those principles, while contrasting them to the constraints of other architectural styles.The software architecture framework of Chapter 1 is used to define the architectural elements of REST and examine sample process, connector, and data views of prototypical architectures. The design rationale behind the Web architecture can be described by an architectural style consisting of the set of constraints applied to elements within the architecture.Additional constraints can then be applied to form a new architectural style that better reflects the desired properties of a modern Web architecture. This section provides a general overview of REST by walking through the process of deriving it as an architectural style.REST has been developed using the latter process. Figures 5-1 through 5-8 depict this graphically in terms of how the applied constraints would differentiate the process view of an architecture as the incremental set of constraints is applied. The Null style (Figure 5-1) is simply an empty set of constraints.

REST stands for Representational State Transfer and API stands for Application Program Interface. REST is a software architectural style that defines the set of rules to be used for creating web services. Web services that follow the REST architectural style are known as RESTful web services.
Your All-in-One Learning Portal: GeeksforGeeks is a comprehensive educational platform that empowers learners across domains-spanning computer science and programming, school education, upskilling, commerce, software tools, competitive exams, and more.It allows requesting systems to access and manipulate web resources by using a uniform and predefined set of rules. Interaction in REST-based systems happens through the Internet's Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).It is a key constraint that differentiates between a REST API and a Non-REST API. It suggests that there should be a uniform way of interacting with a given server irrespective of device or type of application (website, mobile app).It means that the necessary state to handle the request is contained within the request itself and server would not store anything related to the session. In REST, the client must include all information for the server to fulfill the request whether as a part of query params, headers or URI.

REST is an architectural style, or design pattern, for APIs.
What is REST — A Simple Explanation for Beginners, Part 1: Introduction This is part 1 of 2 articles explaining the basic concepts of REST. What you should know before reading this article: You …A RESTful web application exposes information about itself in the form of information about its resources. It also enables the client to take actions on those resources, such as create new resources (i.e. create a new user) or change existing resources (i.e.REST was defined by Roy Fielding, a computer scientist. He presented the REST principles in his PhD dissertation in 2000.Now let’s get back to REST.
REST is an acronym for REpresentational State Transfer and an architectural style for distributed hypermedia systems. Roy Fielding first presented it in 2000 in his famous dissertation. Since then, it has become one of the most widely used approaches for building web-based APIs (Application ...
REST is an acronym for REpresentational State Transfer and an architectural style for distributed hypermedia systems. Roy Fielding first presented it in 2000 in his famous dissertation. Since then, it has become one of the most widely used approaches for building web-based APIs (Application Programming Interfaces).During the development phase, API developers can implement REST in a variety of ways. Like the other architectural styles, REST also has its guiding principles and constraints.The layered system style allows an architecture to be composed of hierarchical layers by constraining component behavior. In a layered system, each component cannot see beyond the immediate layer they are interacting with. A layman’s example of a layered system is the MVC pattern. The MVC pattern allows for a clear separation of concerns, making it easier to develop, maintain, and scale the application. REST also allows client functionality to be extended by downloading and executing code in the form of applets or scripts.REST is not a protocol or a standard, it is an architectural style.
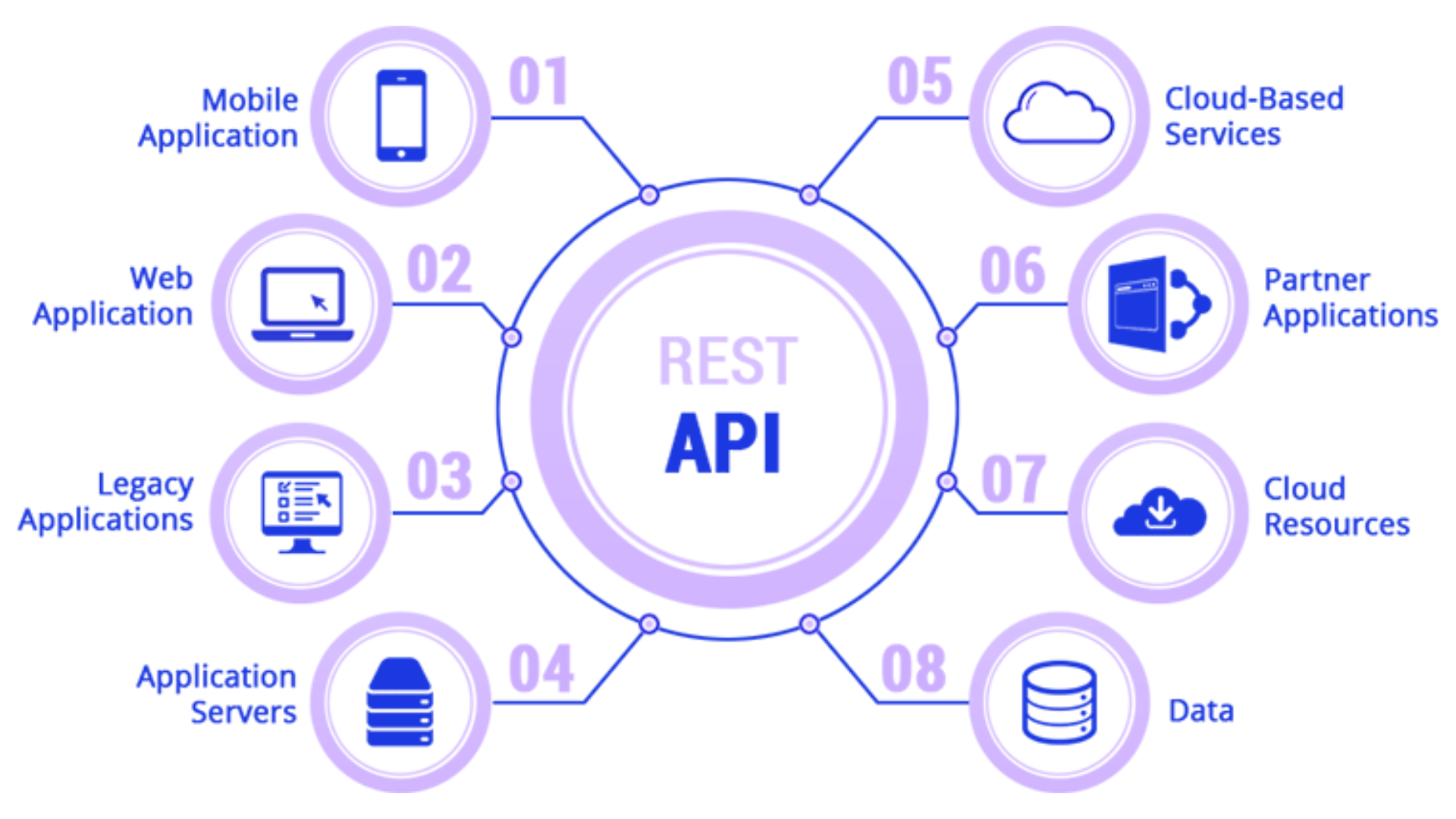
A REST API is an application programming interface (API) that conforms to design principles of the representational state transfer (REST) architectural style.
A REST API is an application programming interface (API) that conforms to the design principles of the representational state transfer (REST) architectural style, a style used to connect distributed hypermedia systems.REST APIs provide a lightweight way to build web APIs and are commonly used to facilitate data exchange between applications, web services and databases, and to connect components in microservices architectures.The application or service that accesses resources is the client, and the application or service that contains the resource is the server. Some APIs, such as SOAP or XML-RPC, impose a strict framework on developers. But developers can develop REST APIs using virtually any programming language and support a variety of data formats.All API requests for the same resource should look the same, no matter where the request comes from. The REST API should ensure that the same piece of data, such as the name or email address of a user, belongs to only one uniform resource identifier (URI).


RESTful systems implement the REST architectural style.
Discover the fundamentals of Rest architecture. Learn how RESTful services enhance web communication and improve application performance.Learn the fundamentals of REST Architecture.Test Rest APIs on real devices with BrowserStack.REST (Representational State Transfer) architecture is a widely accepted framework for designing networked applications.
REST, or REpresentational State Transfer, is an architectural style for providing standards between computer systems on the web, making it easier for systems to communicate with each other. REST-compliant systems, often called RESTful systems, are characterized by how they are stateless and ...
REST, or REpresentational State Transfer, is an architectural style for providing standards between computer systems on the web, making it easier for systems to communicate with each other. REST-compliant systems, often called RESTful systems, are characterized by how they are stateless and separate the concerns of client and server.We want to make an API to keep track of users, venues, and photos of those venues. This site has an index.html and a style.css. Each user has a username and a password. Each photo has a venue and an owner (i.e. the user who took the picture). Each venue has a name and street address. Can you design a REST system that would accommodate:In the REST architectural style, the implementation of the client and the implementation of the server can be done independently without each knowing about the other.Learn about the REST (Representational State Transfer) paradigm and how rest architecture streamlines communication between web components.

REST is a software architectural style that relies on rules that describes how to define and access resources. As we can see on Google Trends, interest in REST is huge. It’s hard to imagine the moderns Internet without RESTful APIs.
As we mentioned, the REST is a software architectural style. On the other hand, it isn’t standardized (like SOAP). It gives a lot of elasticity as it comes to implementation. For example, there is no single and appropriate way to implement pagination. Therefore, REST defines a set of main, general constraints to follow while developing RESTful APIs.Learn about the REST architecture and its most common applications.Statelessness. A RESTful API should be stateless. In simple words, it means that it doesn’t store any information about the user’s session. Therefore, every single request should provide complete data to process it.Layered system. A REST API can consist of multiple layers, eg., business logic, presentation, data access. Moreover, layers shouldn’t directly impact others. Further, the client shouldn’t know if it’s connected directly to the end server or intermediary.


REST uses nouns to represent resources, and HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.) are then used to perform actions on those resources, effectively acting as verbs. If we use verbs in the URI, we are most probably creating an RPC-style method call having a JSON or XML request/response format.
In REST, having a strong and consistent REST resource naming strategy – will prove one of the best design decisions in the long term. Let's discuss.REST APIs use Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) to address resources. REST API designers should create URIs that convey a REST API’s resource model to the potential clients of the API. When resources are named well, an API is intuitive and easy to use.In REST, the primary data representation is called resource.Having a consistent and robust REST resource naming strategy – will prove one of the best design decisions in the long term.
When a client request is made via a RESTful API, it transfers a representation of the state of the resource to the requester or endpoint. This information, or representation, is delivered in one of several formats via HTTP: JSON (Javascript Object Notation), HTML, XLT, Python, PHP, or plain text.
A REST API (also known as RESTful API) is an application programming interface that conforms to the constraints of REST architecture. REST stands for representational state transfer.When a client request is made via a RESTful API, it transfers a representation of the state of the resource to the requester or endpoint. This information, or representation, is delivered in one of several formats via HTTP: JSON (Javascript Object Notation), HTML, XLT, Python, PHP, or plain text.Something else to keep in mind: Headers and parameters are also important in the HTTP methods of a RESTful API HTTP request, as they contain important identifier information as to the request's metadata, authorization, uniform resource identifier (URI), caching, cookies, and more.Though the REST API has these criteria to conform to, it is still considered easier to use than a prescribed protocol like SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol), which has specific requirements like XML messaging, and built-in security and transaction compliance that make it slower and heavier.

In this architectural style, systems interact through operations on resources. Resources include all data and functionality. They are accessed using Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) and acted upon using simple operations. Systems, service interfaces or APIs that comply with the REST ...
In this architectural style, systems interact through operations on resources. Resources include all data and functionality. They are accessed using Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) and acted upon using simple operations. Systems, service interfaces or APIs that comply with the REST architectural style are called RESTful systems (or RESTful APIs).REST was first developed by computer scientist Roy Thomas Fielding in 2000 as part of his Ph.D. dissertation at the University of California, Irvine, titled Architectural Styles and the Design of Network-based Software Architectures.REST (REpresentational State Transfer) is an architectural style for developing web services and systems that can easily communicate with each other.It is popularly believed that REST is a protocol or standard. However, it is neither. REST is an architectural style that is commonly adopted for building web-based application programming interfaces (APIs).

REST is an architectural style designed for constructing distributed systems using hypermedia. It is protocol-independent and not…
REST is an architectural style designed for constructing distributed systems using hypermedia. It is protocol-independent and not inherently associated with HTTP, although most REST API implementations commonly utilize HTTP as the application protocol. Many developers commonly link REST with HTTP, leading to potential confusion.This guide concentrates on crafting REST APIs specifically for HTTP. One key benefit of REST over HTTP lies in its adherence to open standards, avoiding constraints on the API or client application implementation.Every message incorporates adequate information to elucidate its processing, facilitating straightforward analysis by the server. REST APIs adhere to a uniform interface, decoupling client, and service implementations.REST APIs adhere to a stateless request model, emphasizing that HTTP requests must be self-contained and independently processable in any sequence. The absence of transient state information retention between requests enhances scalability by removing the need for client-server affinity, allowing any server to manage requests from any client.

REST, or Representational State Transfer, is the ubiquitous architectural style that answers the pivotal question: how will web servers and clients communicate? Of all the acronyms floating around the world of software engineering, REST is one of the most common.
In the RESTful style, a client requests a resource using a conventionally formatted URL (a RESTful API) and receives back a conventionally formatted JSON response, which describes the resource using key/value pairs.The conventional URL and JSON responses are the distinctive characteristics of modern RESTful web applications. In this style, the URL path describes where an asset exists and the HTTP verb describes how to manipulate it. For example, if you have an API that contains data about music, you might have an endpoint URL like musicservice/albums/1234, where 1234 is the ID of a given asset.As the API grows more complex, the representation of resources becomes less consistent. Let’s say our MusicService API supports tagging albums according to style or genre. You could associate a tag to an album or an album to a tag. In many cases, the approach in a RESTful API boils down to style and preference.When you see a discussion of REST these days, it usually means this kind of RESTful design. Clients are written in JavaScript using one of many available frameworks. Ajax-style requests are often used to drive fine-grained interactions in single-page applications.

Hello WebDevs, I bet whichever framework you have been working on, you must have crossed your roads...
For this Purpose some elite member of society ( Roy Fielding ) created a framework or architectural style called REST. It's very small concept but it becomes difficult when you start using it in real world project and brain consumption becomes equal.Hello WebDevs, I bet whichever framework you have been working on, you must have crossed your roads... Tagged with api, rest, restapi, standard.REST(Representational State Transfer) is a standard that guides the design and development of processes for interacting with data stored on web servers. It simplifies communication by providing various HTTP methods (such as GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) that allow us to perform CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete) on server data.Think of REST as the set of rules that govern how we communicate with servers using the HTTP protocol.






